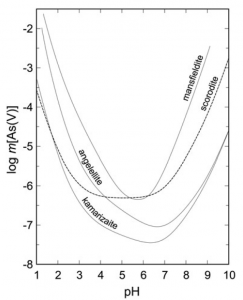
 A complete set of new thermodynamic data has been determined for three Al and Fe arsenate minerals: mansfieldite, angelellite and kamarizaite.
A complete set of new thermodynamic data has been determined for three Al and Fe arsenate minerals: mansfieldite, angelellite and kamarizaite.
Majzlan J., Nielsen U.G., Dachs E., Benisek A., Drahota P., Kolitsch U., Herrmann J., Bolanz R., Števko M. (2018): Thermodynamic properties of mansfieldite (AlAsO4·2H2O), angelellite (Fe2(AsO4)2O3) and kamarizaite (Fe3(AsO4)2(OH)3·3H2O). Mineralogical Magazine 82, 1333-1354. (DOI)




 The findings of this study indicated that the historical mining village of Kaňk is highly contaminated by As, Cu, Pb, and Zn, of which As is the most significant contaminant. Despite the high concencentration of As in mining wastes (∼1.15 wt.%), urban soils (∼0.3 wt.%), and road dusts (∼ 440 mg/kg), risk was associated only with mining waste and contaminated soil material via oral exposure (not the inhalation pathway)
The findings of this study indicated that the historical mining village of Kaňk is highly contaminated by As, Cu, Pb, and Zn, of which As is the most significant contaminant. Despite the high concencentration of As in mining wastes (∼1.15 wt.%), urban soils (∼0.3 wt.%), and road dusts (∼ 440 mg/kg), risk was associated only with mining waste and contaminated soil material via oral exposure (not the inhalation pathway) The re-measurement of mercury (Hg) concentrations in archived environmental samples (soils, peats) after several years of storage indicated that there is no statistical difference between new measurements and original data. As a result, archived samples can be used to evaluate historical soil mercury contamination.
The re-measurement of mercury (Hg) concentrations in archived environmental samples (soils, peats) after several years of storage indicated that there is no statistical difference between new measurements and original data. As a result, archived samples can be used to evaluate historical soil mercury contamination. A combination of multiple techniques including XAS and isotopes helped to decipher the mobility of Tl in mining-polluted desert soil in Namibia. Mechanical transport of fine particles of post-flotation tailings is probably responsible for Tl dispersion in soil profiles.
A combination of multiple techniques including XAS and isotopes helped to decipher the mobility of Tl in mining-polluted desert soil in Namibia. Mechanical transport of fine particles of post-flotation tailings is probably responsible for Tl dispersion in soil profiles.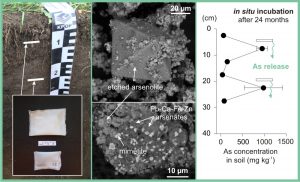 A first long-term (2 years) field experiment indicated how As and other metal(loid) contaminants can be released from As-rich copper smelter flue dust after deposition in contrasting soils. Up to 72% of As was leached out from the flue dust after incubation. The majority of As became highly mobile and could represent a risk for individual environmental compartments (soil, water).
A first long-term (2 years) field experiment indicated how As and other metal(loid) contaminants can be released from As-rich copper smelter flue dust after deposition in contrasting soils. Up to 72% of As was leached out from the flue dust after incubation. The majority of As became highly mobile and could represent a risk for individual environmental compartments (soil, water).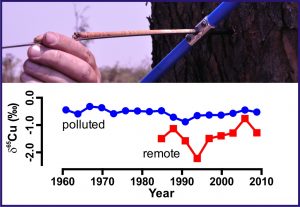 We published first Cu isotope data in pine tree rings and surrounding polluted and unpolluted soils in the Zambian Copperbelt. In highly polluted soil profiles, there is greater Cu isotope fractionation and Cu isotope compositions in tree rings indicate that there was a non-root uptake of Cu uptake by the trees.
We published first Cu isotope data in pine tree rings and surrounding polluted and unpolluted soils in the Zambian Copperbelt. In highly polluted soil profiles, there is greater Cu isotope fractionation and Cu isotope compositions in tree rings indicate that there was a non-root uptake of Cu uptake by the trees. Check the great paper by Petr Drahota and co-authors about low-temperature formation of As sulphides, which has just been published in GCA! Drahota P., Mikutta C., Falteisek L., Duchoslav V., Klementová M. (2017): Biologically induced formation of realgar deposits in soil. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 218, 237-256. (
Check the great paper by Petr Drahota and co-authors about low-temperature formation of As sulphides, which has just been published in GCA! Drahota P., Mikutta C., Falteisek L., Duchoslav V., Klementová M. (2017): Biologically induced formation of realgar deposits in soil. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 218, 237-256. (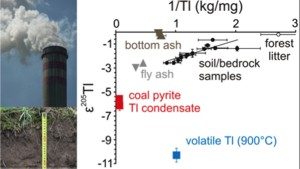 We studied how thallium isotopes can be used for tracing anthropogenic pollution in soils contaminated by emissions from coal-fired power plants. These results are the first published isotope data generated by our brand new MC-ICP-MS lab. Vaněk A., Grosslova Z., Mihaljevič M., Trubač J., Ettler V., Teper L., Cabala J., Rohovec J., Zadorova T., Penizek V., Pavlu L., Holubik O., Nemecek K., Houska J., Drabek O., Ash C. (2016): Isotopic Tracing of Thallium Contamination in Soils Affected by Emissions from Coal-Fired Power Plants. Environmental Science and Technology 50, 9864-9871. (
We studied how thallium isotopes can be used for tracing anthropogenic pollution in soils contaminated by emissions from coal-fired power plants. These results are the first published isotope data generated by our brand new MC-ICP-MS lab. Vaněk A., Grosslova Z., Mihaljevič M., Trubač J., Ettler V., Teper L., Cabala J., Rohovec J., Zadorova T., Penizek V., Pavlu L., Holubik O., Nemecek K., Houska J., Drabek O., Ash C. (2016): Isotopic Tracing of Thallium Contamination in Soils Affected by Emissions from Coal-Fired Power Plants. Environmental Science and Technology 50, 9864-9871. ( In the footsteps of previous research on zýkaite (Majzlan J., Amoako F.Y., Kindlová H., Drahota P. (2015): Thermodynamic properties of zýkaite, a ferric sulfoarsenate. Applied Geochemistry 61, 294-301,
In the footsteps of previous research on zýkaite (Majzlan J., Amoako F.Y., Kindlová H., Drahota P. (2015): Thermodynamic properties of zýkaite, a ferric sulfoarsenate. Applied Geochemistry 61, 294-301, 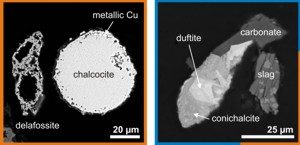 Mobility of metal(loid)s in soils is strongly affected by their binding to solids. We studied smelter- and mining-derived particulates with high levels of metals and metalloids (As, Sb) and their stability in soils from dry semi-arid and wet subtropical areas in Africa. Ettler V., Johan Z., Kříbek B., Veselovský F., Mihaljevič M., Vaněk A., Penížek V., Majer V., Sracek O., Mapani B., Kamona F., Nyambe I. (2016): Composition and fate of mine- and smelter-derived particles in soils of humid subtropical and hot semi-arid areas. Science of the Total Environment 563-564, 329-339. (
Mobility of metal(loid)s in soils is strongly affected by their binding to solids. We studied smelter- and mining-derived particulates with high levels of metals and metalloids (As, Sb) and their stability in soils from dry semi-arid and wet subtropical areas in Africa. Ettler V., Johan Z., Kříbek B., Veselovský F., Mihaljevič M., Vaněk A., Penížek V., Majer V., Sracek O., Mapani B., Kamona F., Nyambe I. (2016): Composition and fate of mine- and smelter-derived particles in soils of humid subtropical and hot semi-arid areas. Science of the Total Environment 563-564, 329-339. (