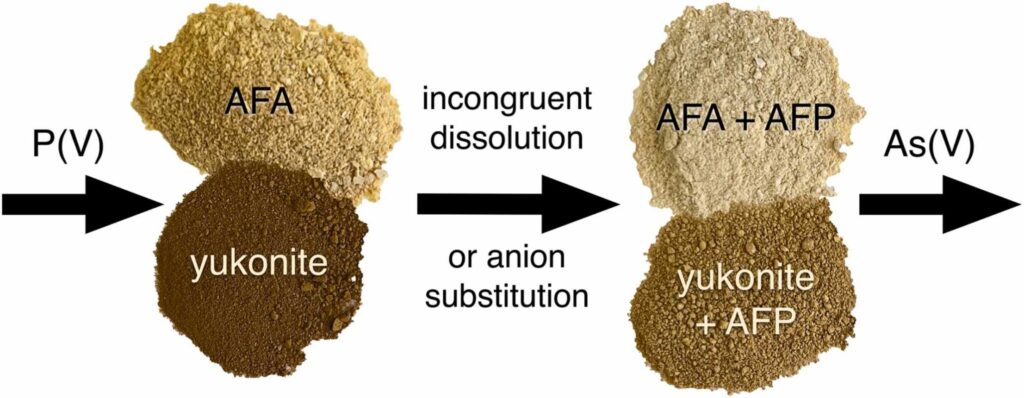
The significant release of arsenic observed from ferric arsenate minerals in the presence of elevated phosphate levels underscores the complexity of their stability in natural environments. Our findings highlight the need to reconsider phosphate treatments in extraction procedures involving ferric arsenates, emphasizing the importance of cautious application in managing polymetallic mine wastes. For sustainable land management, minimizing long-term phosphate additions to arsenic-contaminated soils and mine tailings containing ferric arsenates is crucial to mitigate As(V) export into surface waters and groundwater.
Petra Stubbe (Venhauerova), Irena Matulková, Christian Mikutta, Petr Drahota (2024): Dissolved phosphate decreases the stability of amorphous ferric arsenate and nano-crystalline yukonite. Journal of Hazardous Materials 471, 134374. (DOI)